
flow5 source code
Updated January 1st, 2026
Code structure
Modules
flow5 v7.54 is made up of three modules
- fl5-app: the flow5 main UI application
- fl5-lib: the flow5 solver
- XFoil-lib: the XFoil program
The UI module
This module provides the interface to the pre- and post-processing of the calculations.
It requires the availability of the following libraries:
- OpenCascade development framework
- Gmsh
- LAPACK and BLAS modules which can be provided by various libraries
XFoil
flow5 uses XFoil v6.94 as its 2d boundary layer solver.
The original Fortran source code has been translated to C++ and packaged into a library made of the XFoil class.
This library has been upgraded from xflr5 and is not compatible with the legacy application. Conversely, flow5 requires the upgraded library to run.
If the legacy XFoil-lib is installed as a shared library at user or system level, it should be uninstalled and replaced with the upgraded library.
This library does not have external dependencies.
flow5 solver
The flow5 solver contains all objects and analysis classes to run 2d and 3d calculations.
It is isolated in the library fl5-lib.
The library depends on:
- QtCore library
- OpenCascade development framework
- LAPACK, LAPACKE and BLAS modules which can be provided by various libraries
As of v7.54 this module can be used as a low-level API by external applications.
Installation from source
Integrated Development Environment (IDE) and Qt framework
The recommended IDE to explore and use the source code is QtCreator.
flow5 requires the Qt5 or Qt6 development libraries to compile, and the runtime libraries to run.
Linux:
QtCreator and the Qt development framework are likely provided by the distro's package manager. If not, download them from the Qt website.
Install QtCreator.
Install the Qt6 development libraries, usually identified by a "-dev" or "-devel" suffix.
Windows: QtCreator and the Qt development framework are available from the Qt website.
MacOS: QtCreator and the Qt development framework are available from the Qt website. Alternatively they can be installed via Brew.
External libraries
The section describes the main steps to install the above mentioned external libraries. Note that linkage to the flow5 source code requires:
- at compilation time:
the path to the include directories containing the header (.h) files, and the path to the template libraries (.lib Windows) or the shared libraries (.so Linux and .dylib macOS);
the paths are set in the corresponding OS sections of the .pro files. - at run time: the availability of the shared libraries (.so, .dylib or .dll) in the local PATH.
Linear algebra
flow5 requires the following modules:
- BLAS
- LAPACK
- LAPACKE
Linux:
All libraries are provided by the distribution's package manager.
Install the development version of the following libraries, i.e. with a suffix "-dev" or "-devel":
- openblas
- lapack
- lapacke
Intel's MKL is an alternative which packages all three modules.
OpenBLAS and MKL offer comparable performance.
The install process of the 'standalone' MKL library is a one-click installation procedure.
The selection of either OpenBlas or MKL is made by commenting/uncommenting the instruction CONFIG += INTEL_MKL in the fl5-app.pro and fl5-lib.pro files.
Note that switching from one library to the other requires the re-compilation of the source code.
Windows:
Intel's MKL library is required.
One click install of the 'standalone' package from Intel's website.
MacOS:
The linear algebra libraries are provided by the native "Accelerate" framework. No action required.OpenCascade (OCC)
flow5 v7.54 has been tested with OCC 7.9.2.
Linux:
If your distro provides them, install the OpenCascade development libraries, e.g. occt-dev or occt-devel. The name depends on the distro.
If not, the source code for the OCC framework can be downloaded from the OCC website and must be compiled locally.
Windows
OCC provides a binary package for Windows. Note however that the binary libraries may or may not be compatible with your local compilers, depending on the respective Application Binary Interfaces (ABI). This can lead to undecipherable errors at runtime. If this occurs, compile the libraries locally.
MacOS
The OCC framework can be installed via Brew or compiled from the source code.
If using Brew, the installation of Gmsh will also install OCC.
Compilation and installation
The procedure follows the steps:
- Configuration of the compilation instructions
- Generation of the compilation instructions
- Compilation of the source code
- Installation of the libraries
1. Configuration:
OCC provides CMakeLists to configure the source code for compilation.
The procedure followed here uses CMake-Gui for convenience.
CMake-gui is provided by the distribution in linux, and is available from their website for Windows and MacOS.
- launch CMake-gui
- define the paths to the source code and to the build directory; it is good practice to build in a separate folder.
- select the compilers
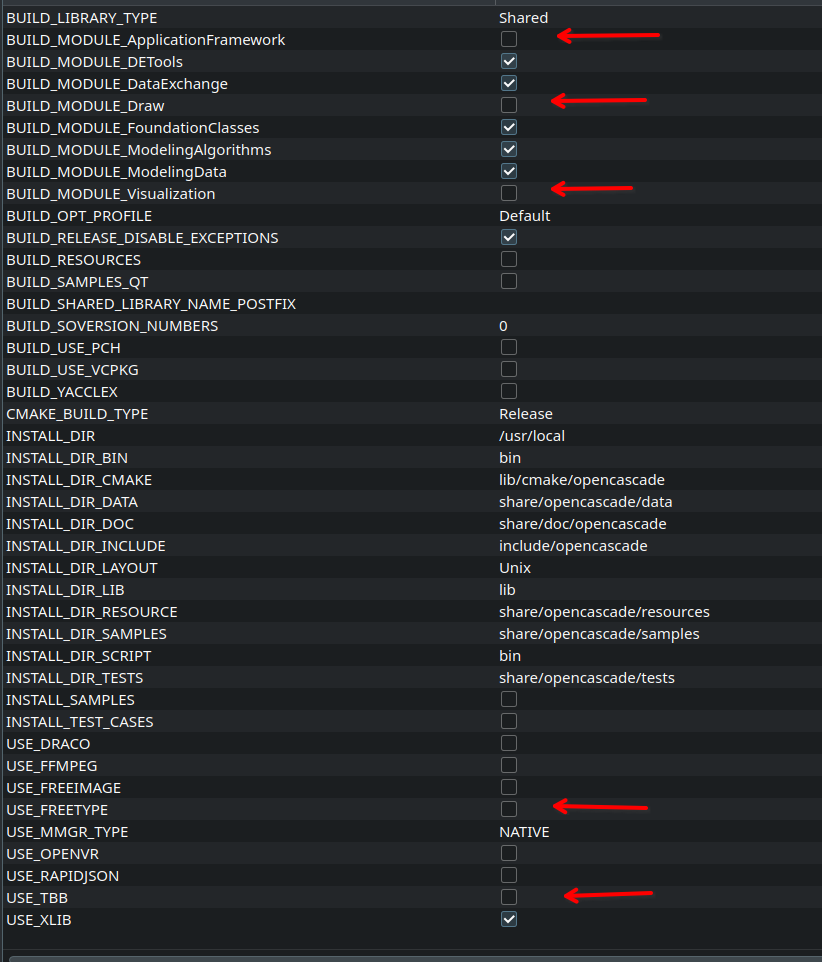
- click "Configure" a first time to load the default CMakeList; the output will turn red.
- Not all modules are required by flow5. Deselect: Application framework, Draw, Visualization, TBB, FreeType.
- click "Configure" again; the output will turn white; some minor warnings may be printed in the bottom output pane.
2. Generation:
Still in the CMake-gui interface, click "Generate".
This will create a MakeFile in the build directory for Linux and MacOS, and a .sln file for Visual Studio in Windows.
In Linux and Mac, open a terminal, move to the build folder i.e. where the makefile is located, and enter:
- make -jN where N is the number of thread allocated to the compilation process; this may take a little time.
In Windows, use Visual Studio to build the solution.
4. InstallationIn Linux and Mac, in the same build folder, enter:
- sudo make install to copy the header files into /usr/local/include/opencascade and the libraries into /usr/local/lib
- sudo ldconfig to register the libraries
In Windows, the simplest is to leave the libraries where they were built and to note the paths to:
- the include directory containing the header (.h) files,
- the lib directory containing the (.lib) template libraries,
- the bin directory containing the (.dll) shared libraries.
Gmsh
flow5 requires the gmsh SDK (not the application!) to run.
flow5 v7.54 has been tested with Gmsh 4.14.1.
Linux: If your distro provides them, install the Gmsh development libraries, e.g gmsh-dev or gmsh-devel. The name depends on the distro.
MacOS: use Brew to install Gmsh; this also install the OCC libraries. Alternatively, a binary package is available for download from the Gmsh website. The package is not notarized so that its usage will require explicit authorisation in the OS.
Windows: A binary package is available for download from the Gmsh website. Check ABI compatibility with the local compilers.
Compilation from source: The procedure is the same as for the OCC libraries. In the configuration phase, activate ENABLE_BUILD_DYNAMIC to build the SDK as a separate module.
flow5
In the relevant OS section of the fl5-app.pro and fl5-lib.pro files, set the paths to the include and library directories of the external dependencies.
Compile in release mode; note that an error may occur if fl5-app compiles before the XFoil or fl5-lib modules. Resume compilation to remove the error.
In Linux, move to the build directory where the MakeFile is located and enter sudo make install to install the libraries in /usr/local/lib. Enter sudo ldconfig to register the libraries.
When flow5 is launched from within QtCreator, the IDE creates a local environment which includes the paths to the shared libraries required at runtime.
When launching flow5 from a shell, the paths must be defined in the user's environment.
In Linux and MacOS, the installation directories in /usr/local/lib or /opt/brew/... are known to the OS and no special action is required.
In Windows, the path to the .dll libraries must be defined in the environment variables.
An alternative in all three OS is to assemble a local package by copying the dependencies manually into the folder containing the flow5(.exe) executable.
Back to top